Customer Data Platform (CDP) Use Cases: How to Generate Value with Data

Article updated on: 23 May 2024
A customer data platform (CDP) is a powerful tool that collects, unifies, and manages data from different sources to create a unified view of the customer. It’s mainly used by marketing and customer service to improve customer experience and drive sales, though it can also be helpful to other departments.
There are many CDP use cases out there, each bringing value to different teams and business contexts. In this guide, we’ll highlight the ones we found most valuable in our work with customers, include examples of our CDP of choice – the SAP Customer Data Platform – and showcase our experiences and results.
The CDP use cases we’ll cover are:
- Customer data unification
- Customer segmentation
- Improved personalization
- Omnichannel customer experience
- Effective loyalty programs
- Retail media efforts
- Data privacy and regulatory compliance
Let’s jump right in!
CDP Use Case #1: Customer Data Unification
Customer data unification includes combining customer data from different sources into a complete customer profile and making it available to the relevant teams.
In our experience working with clients, customer data unification is the most common CDP use case. This is due to companies saving data in various data silos, using mismatching practices for record-keeping, and without having a way to reconcile that data.
The main goal of customer data unification is to create a comprehensive 360-view of your customer by combining first-party and third-party data from different sources such as:
- website or digital commerce analytics
- social media
- mobile app usage
- newsletter subscriptions
- your CRM platform.
-
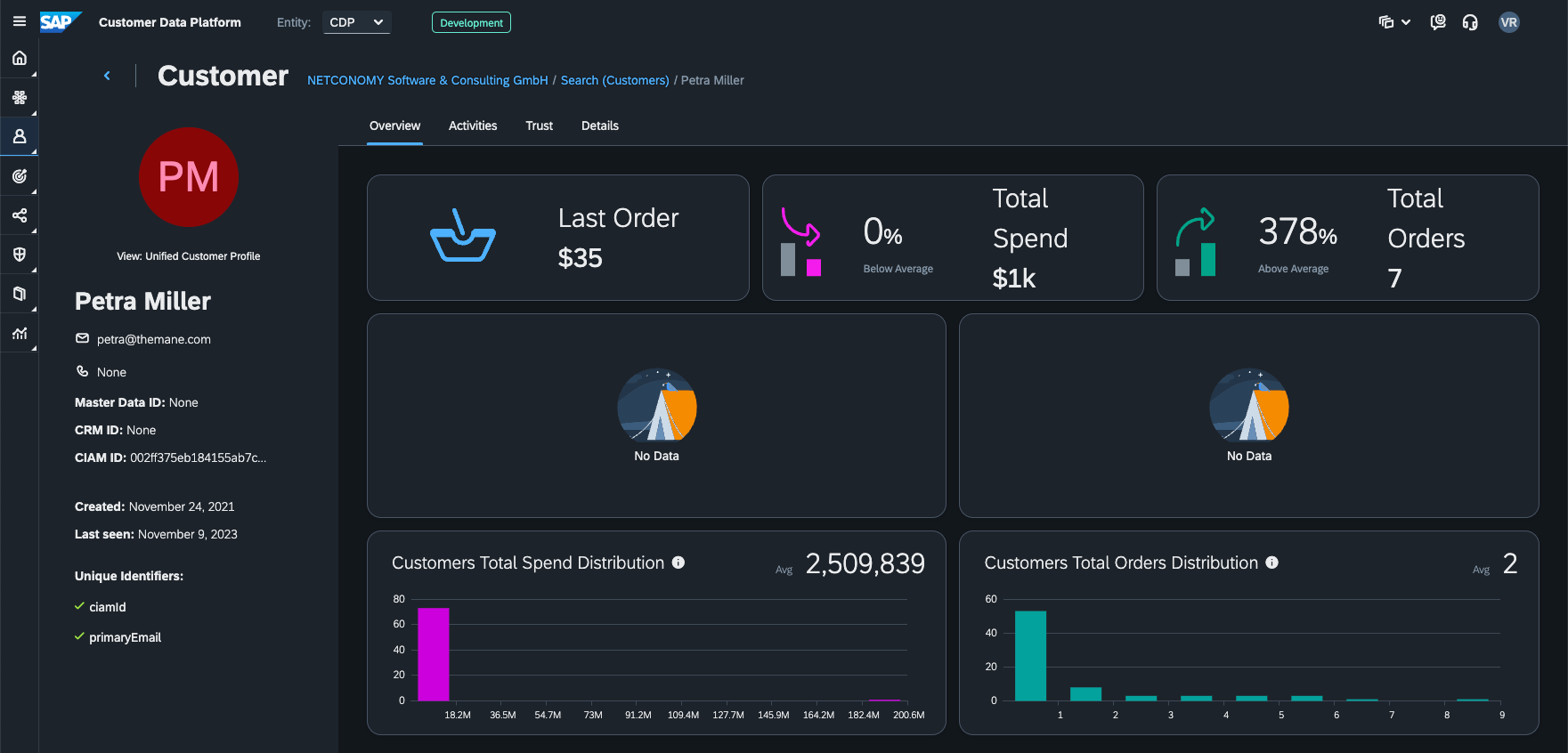
A part of the 360-customer view in SAP CDP - Overview of a 360 customer profile in SAP CDP
In our work with Migros – Switzerland’s biggest retailer – we used a customer data platform to bring together data from millions of customers and create a unified view across the entire company and all its brands.
Before using the CDP, Migros had to manually save and update customer data leading to duplicate or outdated information. To make matters worse, this data was kept in silos across the organization, making it difficult to see the big picture.
By using a customer data platform to create a 360 customer profile, we helped establish a ‘single source of truth’ when it comes to customer data. This helped eliminate organizational data silos and reduced the risk of having outdated or inaccurate data.
CDP Use Case #2: Customer Segmentation
Segmentation is one of the key CDP use cases for marketing, and virtually all solutions on the market offer it.
By dividing customers into cohorts based on demographics, preferences, and behaviors, your marketing team can be more data-driven when designing and implementing their campaigns. This approach leads to an increase in ROI and customer engagement.
-
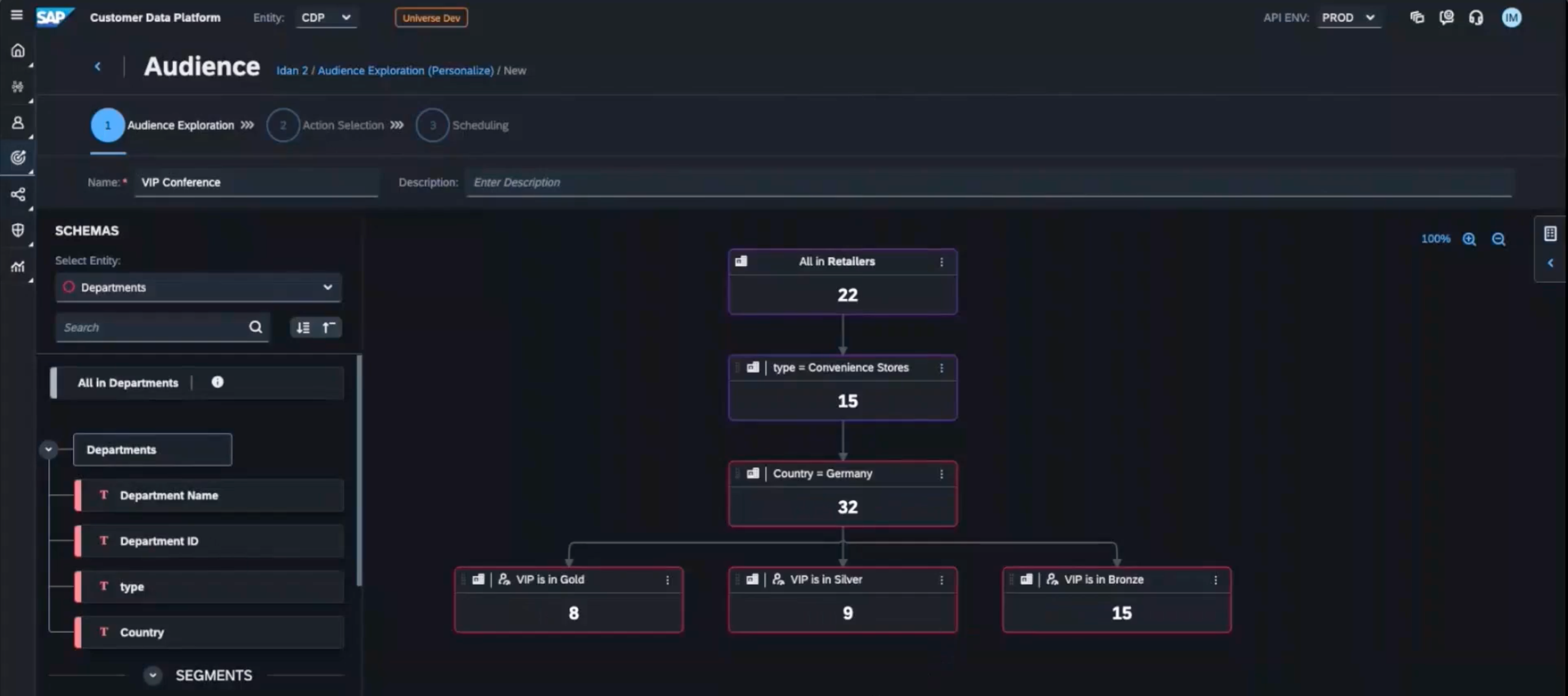
Creating Audience Segments in SAP CDP
Since all your customer data is stored with a customer data platform, it’s ideal for creating customer segments based on different types of data, such as:
- Demographic data: data about your customer’s gender, age, education level, marital status, etc.
- Behavioral data: information about customers’ interactions with your brand, including past purchases, website visits, and social media activity.
- Psychographic data: your customer’s values, interests, attitudes, and other psychological characteristics.
- Geographic data: relevant geographic information, such as city, state, etc., that might affect your customer’s behaviors and preferences.
Another common CDP marketing use case is creating lookalike audiences – groups similar to their company’s existing customers based on demographics or other factors. By using common characteristics like age, gender, or interests, CDPs help your marketing teams find and target new customer groups who might be interested in your products or services.
Next, let’s explore how you can use a CDP to improve your personalization efforts.
CDP Use Case #3: Improved Personalization
Creating a personalized experience for your customers increases the chance of developing long-term customer loyalty and, ultimately – higher sales. Epsilon research shows that 80% of customers reported they are more likely to make a purchase if brands offer them a personalized experience.
However, these experiences are only as good as your customer data – making CDP crucial for personalization efforts across your customer journey.
To illustrate, let’s take something as simple as a website visit.
When customers visit your website, a CDP pulls data on past purchases and interactions and personalizes the homepage. This way, the customer will see products or services they are most likely interested in.
After they make a purchase, the CDP can again use this information to offer complementary products or services. For example, it might offer them an extended guarantee if the customer profile shows that they value this type of security.
On the other hand, the CDP platform will also know what not to do, like promoting this type of product to this specific customer for a set amount of time.
As you can see, a customer data platform is a perfect way to provide personalized experiences using customer data – and a key to building long-term customer loyalty.
CDP Use Case #4: Omnichannel Customer Experience
At a time when an average customer uses three to five channels to make a purchase, it’s easy to understand why it’s crucial to provide consistent experiences across all touchpoints.
By leveraging an omnichannel customer experience, you ensure that:
- Your customers can engage and buy a product when and where it is convenient.
- There are no gaps in the customer journey; customers can pick up where they left off no matter the channel they use.
This convenience improves the overall customer experience, making customers more likely to become loyal and recommend your business to others.
A customer data platform makes it easier to provide truly omnichannel customer experiences by storing all customer data centrally and pushing it to different action platforms.
In our work with Migros, we combined SAP CDP with SAP Emarsys, a marketing automation solution ideal for omnichannel customer journeys. Together, SAP CDP and Emarsys allow Migros to delight customers wherever they are while automating a part of their marketing activities.
You can also empower your in-store teams to provide personalized suggestions to the customer by offering complementary products or services to the one they are picking up.
Next, let’s see how you can make the customer experience even better with super-relevant loyalty programs.
CDP Use Case #5: Effective Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs are a great way to incentivize your customers to make repeat purchases and form an emotional connection with your brand. This is not a small thing, considering loyal customers spend 67% more than new ones, according to Bain and Company.
A customer data platform is an excellent foundation for an effective loyalty program. By unifying your customer’s behaviors, preferences, and past behaviors, a CDP helps you design loyalty programs tailored to your customers.
For example, with a CDP, you can design a loyalty program with rewards and incentives that resonate the most with your most profitable customer segment.
Or, if you have leftover stock of a specific product, you can connect it to a loyalty program and reduce your warehouse costs.
Finally, a customer data platform also helps you measure the effectiveness of your loyalty programs. By tracking customer behavior and engagement over time, you can make data-driven decisions around design and optimization.
While all of these CDP use cases bring value across industries, the next one is crucial for retailers.
CDP Use Case #6: Retail Media Efforts
Retail media is the practice of selling ad space on a retailer’s digital channels, including its website, social media, or mobile applications. Think of it as brand ads within a retail store, only digital.
According to an eMarketer forecast, global retail media spending will surpass $140 billion in 2024, and retailers everywhere are looking to access this rich new revenue stream.
However, only those retailers with access to quality first-party customer data will capitalize on these efforts. Therefore, a customer data platform is essential to any retail media campaign.
Since they combine data from disparate sources, CDPs allow retailers to plan retail media campaigns across all touchpoints, optimize them for maximum results, and track their effectiveness using various KPIs.
CDP Use Case #7: Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
With several high-profile data breaches dominating the headlines in the past couple of years, customers are more careful about the data they share and how companies deal with it.
On the other hand, after the whopping 746 million EUR fine Amazon got served due to a GDPR breach, companies are also paying attention.
A customer data platform can help you ensure customer data privacy and regulatory compliance in several ways.
By storing all customer data centrally, CDPs ensure it is safe and protected from unauthorized access. For this purpose, they offer security measures such as encryption, access controls, and monitoring.
Customer data platforms often include features that allow you to store data and manage consent in accordance with specific regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
To simplify customer data management even further, we advise our customers to always use SAP CDP and CDC (Customer Data Cloud) together. This combination ensures that customer data is always protected from the moment the customer fills out the registration form.
These platforms give you the tools to receive and record customer consent for data collection and answer customer requests to access, delete, or modify their data.
Final Thoughts on Customer Data Platform Use Cases
There are many customer data platform use cases that can bring value to your company.
The most basic ones start by unifying your customer data from various sources into a comprehensive 360 customer profile.
Your marketing team can then use the data to create customer segments and offer personalized omnichannel experiences that drive revenue.
Finally, a CDP is an excellent foundation for both loyalty and retail media programs and a must for companies looking to stay compliant with global customer data protection regulations.
No matter which CDP you opt for, make sure it covers the use cases specific to your business model and context, and that will bring you the most value.
This will help you make an informed decision and save you a lot of headaches down the road.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Customer Data Platform Use Cases
What is the use case of CDP in retail?
Customer data platforms are crucial for retailers as they help them collect and unify customer data coming from many different sources. Retail marketers can then use this data for targeted campaigns, better personalization efforts, or loyalty programs. A new CDP use case for retailers which is quickly gaining attention is around retail media – the process of selling ad space on retailer’s digital channels.
What is the most common use case of CDP?
Based on our experience, the most common use case for a CDP is collecting customer data from different sources and unifying it into a comprehensive 360 customer profile. This is closely followed by CDP use cases for marketing like customer segmentation and personalization.
How is CDP used in B2B companies?
B2B companies can use a customer data platform in a similar way B2C companies do – from unifying customer data to providing personalization options or loyalty programs. A major difference is that the CDP tracks not only individual customer data, but also department and company-level data to provide the full picture of a customer organization.
Authors and Contributors

Valentin Rabitz | Solution Architect, NETCONOMY